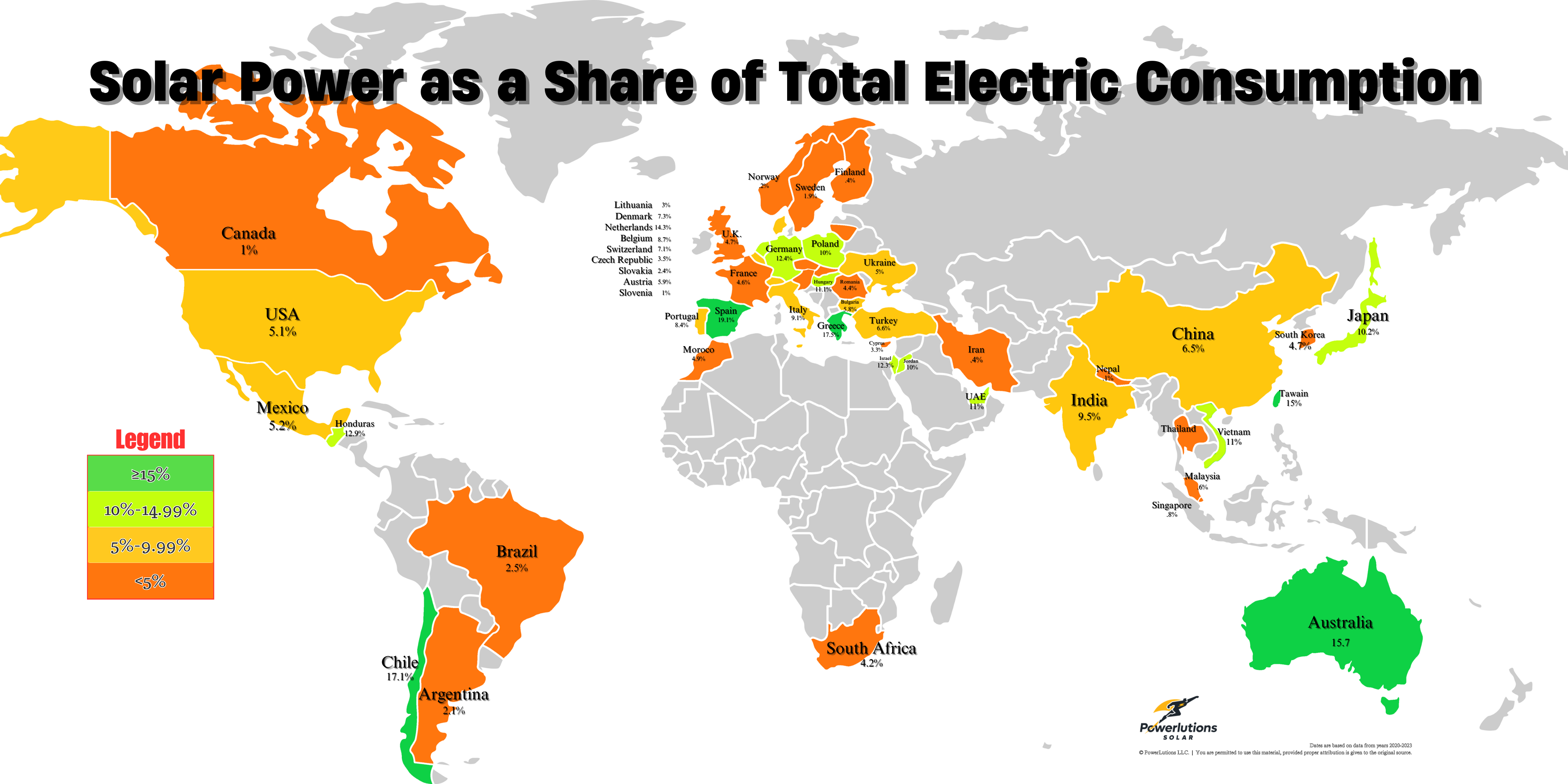
As we progress further into the 21st century, an energy revolution is well underway across the globe. Traditional energy sources are being phased out in favor of cleaner, renewable alternatives, and leading this charge is solar power—the process of converting light from the sun into usable electricity.
Solar power isn't just about powering our homes, cars, and businesses sustainably—it's also a potent weapon in our arsenal against climate change. Countries around the world are recognizing this and are investing heavily in this thriving sector.
Let's take a look at the latest statistics and projections that paint the picture of the global solar power market today. We'll delve into the market size, growth, power generation, capacity, current trends, and future forecasts.

Global Solar Power Market Overview
The solar power market has seen explosive growth recently. As of 2023, the global solar power market is valued at about USD 175.6 billion, and some estimate that it is set to reach an estimated USD 256.2 billion by 2028.
This remarkable expansion reflects an enduring upward trajectory in the market with the global solar electricity market projected to grow from USD 87.07 billion in 2022 to USD 106.62 billion in 2023—an impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.5%.
Solar power has become the fastest-growing electricity source in the U.S., representing 54% of generation projects planned for 2023. Globally, solar PV capacity additions in 2021 were largely contributed by utility-scale plants, which accounted for 52% of global solar PV capacity additions in that year.
In terms of global renewable capacity, a record increase is set to occur—with additions expected to soar by 107 gigawatts (GW), the largest absolute increase ever, totaling more than 440 GW in 2023.
Substantial growth has also been observed in residential solar power, progressively becoming a popular choice among households worldwide. The global solar electricity market also confirms this trend, showing an overall increase from $87.07 billion in 2022 to $106.62 billion in 2023, indicating a compound annual growth rate of 22.5%. SEIA forecasts an approximate growth of home solar power around 6,000 to 7,000 MW per year between 2023 and 2027. These statistics reveal an uptrend in the residential solar power sector, becoming an attractive and effective energy choice globally.
The future of solar power seems radiant, with some estimates predicting the global solar energy market will mushroom to a staggering 422 billion U.S. dollars. Projections and forecasts predict an ever brightening future for solar power across the globe.
The booming global solar power market sets the stage for our next round of discussions where we investigate how various global regions are adopting, utilizing, and benefiting from this forward-looking technology. Stay tuned as we shed light on the state of solar power around the world.
The Impact of Solar Power
As the world increasingly leans towards renewable energy sources, solar power is playing an instrumental role in transforming the energy landscape. From mitigating climate change to innovative uses, solar power is making waves worldwide. The promise of solar energy, particularly in the context of energy independence, is being increasingly recognized. Solar energy enables consumers and nations alike to be less reliant on traditional energy sources and imports, bringing an unprecedented level of autonomy.
Solar power plays a critical role in mitigating climate change. In 2023, global energy-related carbon dioxide emissions rose by less than 1%. This lower-than-anticipated rise was attributed to the growth of clean energy technologies, like solar power. Furthermore, solar energy contributes significantly to greenhouse gas reductions, as renewable energy sources like solar emit little to no greenhouse gases. To put things into perspective, even when accounting for life-cycle emissions (from manufacturing to disposal), solar panels reduce CO2 emissions more per acre than trees do. Such stats underline solar power’s huge positive impact on the environment.
Solar power is making meaningful strides as it lights the path towards global energy independence. Its continued integration into power grids encourages a strong transition from traditional energy resources. Symbols of this revolution are evident in increasing efficiency levels of solar cells, panels, and batteries, contributing to both price and supply stability.
Driving this shift, the United States has seen a decline in total energy imports in recent years as increases in domestically produced energy, including solar, offset the need for foreign resources. A similar trend is observed in Europe, where investing in renewables has proven beneficial for their energy security and independence, reducing reliance on imports while ensuring a sustainable energy supply.
However, addressing energy independence isn't just about leveraging solar power for electricity generation. It's also about the potential for surplus power to feed back into the grid. This creates a dynamic exchange, where the energy contributed doesn't go to waste but rather supports and stabilizes the broader energy network. For instance, homes equipped with solar panels can produce electricity not just for personal consumption, but also for distribution to neighbors, fostering a sense of community interdependence.
Innovation in solar power usage is reaching new heights. Solar Impulse, a Swiss long-range solar-powered aircraft, achieved a significant milestone as it completed the first round-the-world solar-powered flight, showcasing the potential of renewable energy sources. Moreover, NASA successfully tested solar-powered flights on Mars with its Ingenuity Helicopter, further demonstrating solar technology's versatility and resilience. The aviation industry, which accounted for over 2% of global energy-related CO2 emissions, can significantly benefit from solar-powered flights, contributing to significant CO2 emissions reduction.
Continuing innovation in solar power has seen the emergence of new technologies like transparent solar panels, fusion power breakthroughs, and advancements in wave energy in 2023. Additionally, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly being implemented for solar panel optimization, predictive maintenance, solar forecasting, and energy storage optimization. Further developments in photovoltaic technology have led to an increase in panel conversion efficiency from 15% to over 20% in 2023.
Case Studies: Morocco And India
Morocco has become a clear leader in the realm of solar power. As of 2023, the country is well on its way to achieving a renewable energy target of 52% by 2030. This progress is in part due to Morocco phasing out some fossil fuel subsidies and investing actively in solar power infrastructure. Additionally, Morocco has been leveraging its geography, building a $9 billion Ouarzazate Solar Power Station in the Sahara desert.
India has also been forging ahead with harnessing solar power. As of 31 May 2023, the country's solar installed capacity was an impressive 67.82 GWAC. During COP26 in November 2021, India announced 2030 targets of 500 GW of total non-fossil capacity and 50% renewable electricity generation. In 2022, solar and wind energy have constituted 92% of India's power generation capacity additions, demonstrating a monumental shift away from fossil fuels.
As we delve deeper into the world of renewable energy, it is essential to recognize how varying geographic, economic, and social contexts influence the harnessing of these resources. This section provides a comparative analysis detailing how distinct regions worldwide are exploiting solar power - the challenges they face, the progress they've made, and the trailblazers leading the charge.
Asia:
In Asia, significant progress has been made in the solar power field, particularly by China and India. However, a significant challenge faced in several Asian countries including those in South Asia like India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, and Bhutan, is the availability of financial support and channels, especially for smaller scale solar power projects. Additionally, there are developmental challenges, including, but not limited to, regional policy, interconnected national grids, and the topographical diversity present in many South Asian nations.
Europe:
European countries demonstrate a notable push towards the exploitation of solar power. Challenge-wise, competition for the utilization of land resources with other sectors, skill shortages, and certain technical issues stand out as the primary concerns. The need to align solar power implementation strategies with conservation goals is also becoming critical, particularly to prevent energy poverty and ensure equitable accessibility.
Africa:
In Africa, nations struggle with solar technology's financial aspects, including the necessary investments for infrastructural development and the high up-front costs of solar setups. Also, problematic is the current governance-related risk, which marks complex bureaucracy and changing regulation as a deterrent to private investment in renewable energy projects.
Americas:
In the Americas, numerous programs incentivize clean energy innovation and the implementation of solar power. However, challenges involve maintaining a reliable supply of electricity given the intermittent nature of solar power and ensuring the grid can handle the influx of solar electricity. Additionally, regions are grappling with technical and bureaucratic considerations, particularly pertaining to the rapid expansion of solar projects.
South Pacific:
In the South Pacific region, while the utilization of solar energy is quite high, especially in Australia, there exist significant challenges relating to implementation, largely due to geographical and social exclusivity. Geographic isolation creates impediments for interconnected national grids which makes powering remote island areas through shared resources a difficult endeavor. There are also matters of finance and capacity development specific to renewable energy projects.
Middle East:
Lastly, in the Middle East, the pursuit of solar power dovetails with specific social and political contexts. Challenges typically manifest as financial constraints and socio-political factors impacting the progression and sustainability of solar power projects. Moreover, there are tensions concerning land rights and solar farm installations, entwining environmental concerns with socio-economic objectives.
The adoption of solar power is on an encouraging upward trend globally. However, each region faces a unique set of challenges - financial, technological, and socio-political. These hurdles highlight the complexities involved in the move towards sustainable energy alternatives. The insights gained from studying these challenges will provide valuable direction for the next part of our discussion, where we'll focus further on the future prospects and impact of solar power.
Future Prospects of Solar Power
Solar power continues to grow as a primary source of renewable energy, with exciting prospects anticipated for the future. Expert predictions and current data indicate several key patterns that will shape the next phase of solar energy growth:
The future prospects for solar power are promising, reflecting the global urgency to transition towards more sustainable and renewable energy sources. However, like any other sector, the solar power industry's future is not without challenges. Understanding these patterns and planning for these challenges can potentially guide policymakers, industry, and consumers on a sustainable and prosperous path. As we continue to explore solar power's future, the key lesson is that the evolution of solar technology is not merely a technological journey but a societal one.
Ignite the Spark: Solar Power Amplifying a Brighter Future
Using solar power is about so much more than just creating energy. It's about paving the path for a resilient future that thrives on sustainability and innovation. Solar energy brings to the table significant perks: it empowers us to form viable energy solutions and slash greenhouse gas emissions. It can even play a changing role in greener transportation and branch out to collaborate with new sustainable avenues, such as hydrogen gas production.
However, a brighter future powered by the sun is a collaborative effort, and it's vital for all countries to partake. Countries falling behind in the solar race need a big nudge to start making meaningful strides. At the same time, those with resources should lead by example, using their wealth and knowledge to swing into action, invest in clean energy, and inspire others.
Even for nations where renewable energy is still in its infancy, pitching in is crucial. Solidarity is the key here - wealthier countries teaming up to aid their less developed counterparts, creating resources and opportunities, and making the solar transition possible for everyone.
It's worth keeping in mind that this isn't just a government or corporate-level mission. We're all in this together. Each of us can play a part, staying tuned into policy matters, demanding action from legislators, cheering on companies going green, and doing our small bit to limit our carbon footprints.
Some key elements to focus on:
It's about time we started viewing solar power as a lot more than an attractive alternative. It's a sustainable, clean, and green 'norm' we should be striving for, for our sake and the planet. Now is the time to step up our solar game, and the benefits will extend to generations to come.
Zero $ out
of pocket
Max credits
incentives
Honest &
transparent
14 years of
100% solar
1. Estimate savings on your energy use 2. Leverage the best state incentives
Try our Layout Design Tool!
MAIN OFFICE
216 River Avenue
Lakewood, NJ 08701
732-987-3939
NEW JERSEY
2 University Plaza #100-1
Hackensack, NJ 07601
201-624-9696
NEW YORK
56 South Main St Suite #2
Spring Valley, NY 10977
845-553-7100
NYC
1310 Coney Island Ave
Brooklyn, NY 11230
718-502-3200
MIAMI FLORIDA
66 West Flagler Street
Suite 900-3747
Miami, FL 33130
786-732-3306